AI Explainability 360
A comprehensive open-source toolkit for interpretable and explainable AI across the model lifecycle.
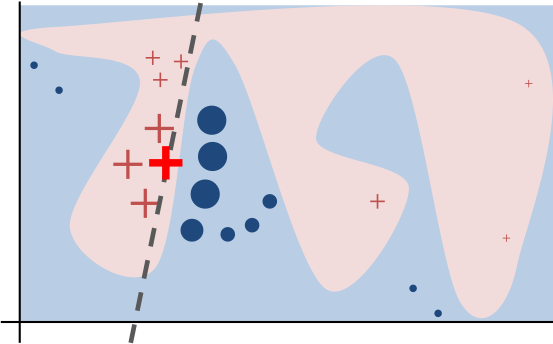
Enable trust and transparency in black-box models through local interpretable surrogate explanations.
LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) is a foundational open-source framework in the field of Explainable AI (XAI) that allows developers and data scientists to explain the predictions of any machine learning classifier or regressor. By treating models as black boxes, LIME perturbs input data points and observes the resulting changes in output to learn a local, interpretable linear model around a specific instance. In the 2026 AI market, LIME remains a critical tool for regulatory compliance (such as GDPR's 'right to explanation') and model debugging. It excels in high-stakes environments like healthcare and fintech, where understanding why a model made a specific decision—such as rejecting a loan or flagging a medical anomaly—is as important as the prediction itself. The library supports a wide array of data types including tabular, text, and image data, and remains model-agnostic, meaning it can interface with Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, PyTorch, and proprietary LLMs. Its 'Submodular Pick' feature further allows for a representative overview of the model's global behavior by selecting a diverse set of local explanations, bridging the gap between local and global interpretability.
Uses a perturbation-based approach to probe models without requiring access to internal weights or gradients.
A comprehensive open-source toolkit for interpretable and explainable AI across the model lifecycle.
Unveiling and Manipulating the Internal Representations of Generative Adversarial Networks
Verified feedback from the global deployment network.
Post queries, share implementation strategies, and help other users.
Algorithms that select a set of representative instances with their explanations to provide a non-redundant global view.
Uses super-pixels to highlight specific regions of an image that contributed most to a classification.
Employs a bag-of-words approach on perturbed text samples to identify words with high predictive weight.
Utilizes K-LASSO to select the most important features in the local surrogate model.
Automatically handles categorical features in tabular data by perturbing based on the distribution of the training set.
Allows users to define custom distance metrics (kernels) to determine the size of the 'neighborhood' for explanations.
Financial institutions must explain to rejected applicants why their loan was denied.
Registry Updated:2/7/2026
Generate a report for the customer.
Radiologists need to know which part of an X-ray led an AI to flag a potential tumor.
A model is flagging neutral text as 'Toxic' due to specific word bias.